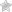Introduction to SQL Commands (DDL, DML,DQL, DCL, TCL)
Beginner-Friendly Professional Documentation
1. SQL Basics & Command Categories
What is SQL?
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a standard language used to manage and interact with databases. Databases store data in the form of tables (rows and columns).
Example: A table called Students may contain columns like:
● StudentID
● Name
● Age
● Course
SQL helps us perform tasks such as:
● Creating tables
● Adding data into tables
● Reading data from tables
● Updating and deleting records
● Controlling database security
● Managing transactions (commit/rollback)
2. Why SQL Commands Matter
SQL is made up of different commands, each used for a specific purpose.
For example:
● To create a table → CREATE
● To insert data → INSERT
● To read data → SELECT
● To allow permissions → GRANT
3. Categories of SQL Commands
SQL commands are grouped into five major categories:
Category |
Full Form |
Purpose |
DDL |
Data Definition Language |
Defines database structure (tables, schema) |
DML |
Data Manipulation Language |
Inserts, updates, deletes data |
DQL |
Data Query Language |
Retrieves (queries) data |
DCL |
Data Control Language |
Controls access/permissions |
TCL |
Transaction Control Language |
Manages transactions (commit/rollback) |
Concepts :
● DDL = Build structure
● DML = Change data
● DQL = Read data
● DCL = Control access
● TCL = Confirm/undo changes
4. DDL (Data Definition Language)
DDL commands are used to create and modify database structure.
That means you use DDL to create tables, change columns, and remove tables.
Key DDL Commands:
● CREATE
● ALTER
● DROP
● TRUNCATE
3.1.CREATE: Used to create a new table.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
CREATE TABLE students ( student_id INT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(50), age INT, course VARCHAR(30) ); This creates a table named students. |
1.1.ALTER: Used to modify an existing table.
Example: Add a new column:
|
1 2 |
ALTER TABLE students ADD email VARCHAR(50); This adds an email column. |
1.3.DROP: Used to completely delete a table.
|
1 2 |
DROP TABLE students; Warning: This removes the table + all data permanently. |
1.1. TRUNCATE: Deletes all rows inside a table but keeps the table structure.
|
1 2 |
TRUNCATE TABLE students; Table remains, but data is removed. |
Summary of DDL:
Command |
Action |
CREATE |
Creates tables/objects |
ALTER |
Modifies structure |
DROP |
Deletes object/table fully |
TRUNCATE |
Deletes all rows but keeps table |
5. DML (Data Manipulation Language)
DML commands are used to work with the data inside tables.
Key DML Commands:
● INSERT
● UPDATE
● DELETE
3.2.INSERT: Adds new data into a table.
|
1 2 |
INSERT INTO students (student_id, name, age, course) VALUES (1, 'Ayesha', 20, ‘B.Tech'); Adds a record. |
3.3.UPDATE: Updates existing records.
|
1 2 |
UPDATE students SET age = 21 WHERE student_id = 1; Updates age for student_id = 1. |
3.4.DELETE: Deletes specific records.
|
1 2 |
DELETE FROM students WHERE student_id = 1; Removes only the selected student record. |
6. DQL (Data Query Language)
DQL is used to retrieve (read) data from the database.
Key DQL Command:
● SELECT
3.5.SELECT: Fetch data from a table.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
SELECT * FROM students; Shows all records. Fetch selected columns: SELECT name, course FROM students; Using condition: SELECT * FROM students WHERE course = 'B.Tech'; Sort results: SELECT * FROM students ORDER BY age DESC; |
Summary of DML & DQL:
Categor y |
Focus |
Commands |
DML |
Modify data |
INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE |
DQL |
Retrieve data |
SELECT |
7. TCL (Transaction Control Language)
TCL commands are used to manage transactions.
What is a Transaction?
A transaction is a group of SQL operations
Key TCL Commands:
● COMMIT
● ROLLBACK
● SAVEPOINT
7.1.COMMIT: Saves the changes permanently.
|
1 2 |
COMMIT; After commit, changes cannot be undone. |
7.2.ROLLBACK: Undo changes (only possible before commit).
|
1 2 |
ROLLBACK; Restores the database to previous state. |
7.3.SAVEPOINT: Creates a point where you can rollback partially.
|
1 2 3 |
SAVEPOINT sp1; Rollback to savepoint: ROLLBACK TO sp1; |
8. DCL (Data Control Language)
DCL is used to manage permissions and security.
Key DCL Commands:
● GRANT
● REVOKE
3.6.GRANT: Gives permission.
|
1 2 |
GRANT SELECT ON students TO user1; Now user1 can read students table. |
3.7.REVOKE: Removes permission.
|
1 2 |
REVOKE SELECT ON students FROM user1; Removes user access. |
9. Final Comparison Table
Type |
Used For |
Example Commands |
DDL |
Structure creation/modification |
CREATE, ALTER, DROP, TRUNCATE |
DML |
Changing data |
INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE |
DQL |
Querying/reading data |
SELECT |
TCL |
Transaction handling |
COMMIT, ROLLBACK, SAVEPOINT |
DCL |
Access control/security |
GRANT, REVOKE |
Conclusion
● DDL builds database structure
● DML changes table data
● DQL reads data
● TCL controls transaction safety
● DCL ensures security and permission control
This makes SQL powerful for real-world applications like:
● Banking systems
● Employee databases
● College record systems
● E-commerce websites
Author : Khaja Shaik
LinkedIn : http://linkedin.com/in/shaik-khajask
Thank you for giving your valuable time to read the above information. Please click here to subscribe for further updates.
KTExperts is always active on social media platforms.
Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/ktexperts
LinkedIn : https://www.linkedin.com/company/ktexperts/
Twitter : https://twitter.com/ktexpertsadmin
YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/c/ktexperts
Instagram : https://www.instagram.com/knowledgesharingplatform