PostgreSQL
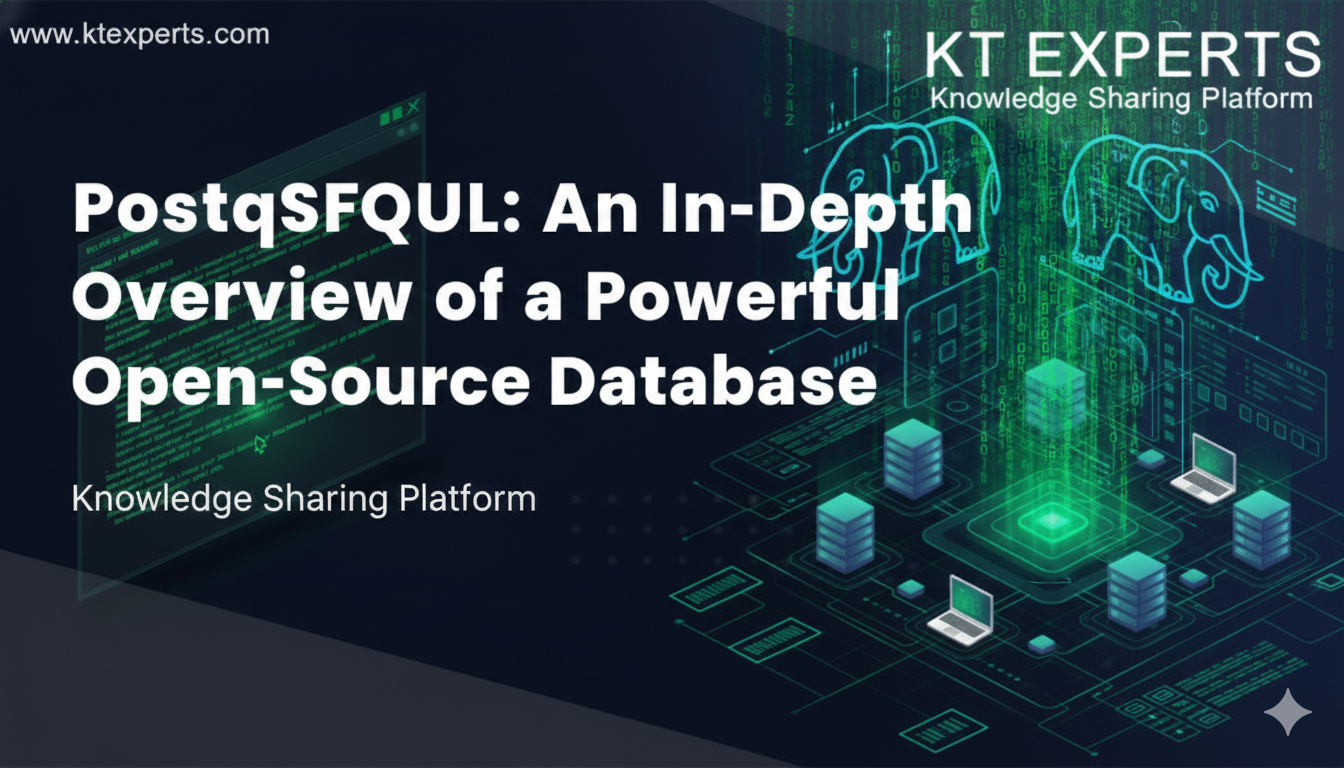
This document is written for absolute beginners. It explains, in a step-by-step and theory-oriented manner, how CSV files are loaded into PostgreSQL and prepared using basic SQL queries before being used. Each section is explained in simple language while maintaining professional and industry-standard terminology.
1. Introduction
PostgreSQL is a powerful, open-source relational database management system (RDBMS). It is designed to store, manage, and retrieve structured data efficiently. Unlike file-based storage systems, PostgreSQL enforces rules through schemas, tables, and data types, ensuring data consistency and reliability.
In PostgreSQL, data is stored in tables composed of rows and columns. Users interact with these tables using SQL (Structured Query Language). SQL allows users to retrieve specific data, filter records, and perform operations such as counting, sorting, and pattern matching.
2. Loading CSV Files into PostgreSQL
CSV files are commonly used to store structured data, but they lack the ability to enforce data types and constraints. PostgreSQL provides a way to import CSV data into tables, allowing the database to manage the data in a structured and queryable format.
Before loading a CSV file, a table must be created in PostgreSQL. For beginner-friendly workflows, columns are often defined as TEXT to avoid import errors caused by mismatched data formats.
Once the table is created, the CSV file can be loaded using the PostgreSQL \copy command. This command reads the CSV file from the local system and inserts the data into the table.
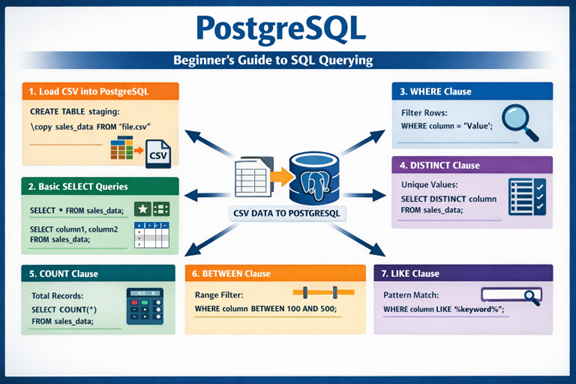
The below Screen shot shows the example raw data that was designed using excel sheet for data sets and then this raw data is loaded to database as follows:
● Create a staging table:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
CREATE TABLE sales_data ( row_id TEXT, order_id TEXT, order_date TEXT, ship_date TEXT, ship_mode TEXT, customer_id TEXT, customer_name TEXT, segment TEXT, region TEXT, product_name TEXT, sales TEXT ); |
● Load CSV into PostgreSQL:
|
1 2 3 4 |
\copy sales_data FROM '/Users/username/Desktop/sales.csv' DELIMITER ',' CSV HEADER; |
3. Basic SELECT Queries in PostgreSQL
The SELECT statement is the most fundamental SQL command in PostgreSQL. It is used to retrieve data from one or more columns of a table. Understanding SELECT queries is essential for working with any PostgreSQL database.
Using SELECT *, all columns from a table can be retrieved. However, best practice is to explicitly specify column names to improve readability and performance.
|
1 2 3 |
SELECT * FROM sales_data; SELECT order_id, sales FROM sales_data; |
4. Where Clause Queries in PostgreSQL
The WHERE clause is used to filter rows based on specified conditions. Filtering allows users to retrieve only relevant records from a table.
|
1 |
SELECT * FROM sales_data Where sales > 10000; |
5. DISTINCT Clause for Dimension Validation
The DISTINCT clause retrieves unique values from a column. For Tableau dashboards, this is essential for validating categorical dimensions such as regions or product types.
Example:
|
1 2 |
SELECT DISTINCT region FROM sales_data; |
6. COUNT Clause for Data Volume Analysis
The COUNT clause is used to determine the total number of records. This is commonly used in Tableau to display KPIs such as total orders or transactions.
|
1 2 |
SELECT COUNT(*) AS total_records FROM sales_data; |
7. BETWEEN Clause for Range-Based Filtering
BETWEEN is used to filter numeric or date ranges. Applying this logic at the PostgreSQL level ensures that Tableau dashboards work with focused and relevant data.
|
1 2 3 |
SELECT order_id, sales FROM sales_data WHERE sales::NUMERIC BETWEEN 500 AND 2000; |
8. LIKE Clause for Text-Based Filtering
LIKE enables pattern-based text searches. It is frequently used to filter product or customer names before visualization in Tableau.
|
1 2 3 |
SELECT order_id, product_name FROM sales_data WHERE product_name ILIKE '%chair%'; |
9. Advanced Filtering with BETWEEN and LIKE
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
SELECT order_id, sales FROM sales_data WHERE sales::NUMERIC BETWEEN 4000 AND 15000; SELECT order_id, product_name FROM sales_data WHERE product_name ILIKE '%Table%'; |
These filtering techniques allow users to retrieve precise subsets of data and are essential skills for working with PostgreSQL databases.
Conclusion
Using PostgreSQL as a preprocessing layer for Tableau ensures scalability and data accuracy. By combining theoretical understanding with practical SQL commands such as DISTINCT, COUNT, BETWEEN, and LIKE, analysts can confidently build professional Tableau dashboards.
Author : Khaja Shaik
LinkedIn : http://linkedin.com/in/shaik-khajask
Thank you for giving your valuable time to read the above information. Please click here to subscribe for further updates.
KTExperts is always active on social media platforms.
Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/ktexperts
LinkedIn : https://www.linkedin.com/company/ktexperts/
Twitter : https://twitter.com/ktexpertsadmin
YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/c/ktexperts
Instagram : https://www.instagram.com/knowledgesharingplatform
Note: Please test scripts in Non Prod before trying in Production.