PostgreSQL: An In-Depth Overview of a Powerful Open-Source Database
In today’s data-driven world, databases play a crucial role in storing, managing, and processing information efficiently. Almost every modern application—whether a web application, mobile app, enterprise system, or research platform—relies on a database at its core. Among the many database systems available, PostgreSQL stands out as one of the most reliable, feature-rich, and advanced open-source database management systems.
PostgreSQL is an object-relational database management system (ORDBMS) that originated from the POSTGRES project developed at the University of California, Berkeley. Over decades of continuous development, it has evolved into a robust and highly trusted database platform used by startups, enterprises, and research institutions across the globe.
What Makes PostgreSQL Special?
PostgreSQL supports a large portion of the SQL standard while also providing advanced features beyond traditional relational databases. It is designed to handle both simple and highly complex data workloads with equal efficiency. Its key capabilities include support for complex queries and subqueries, strong data integrity using constraints and foreign keys, triggers and updatable views for advanced database logic, full ACID compliance for reliable transactions, and Multiversion Concurrency Control (MVCC) for high performance in multi-user environments.
MVCC allows multiple users to read and write data simultaneously without conflicts. Readers do not block writers, and writers do not block readers, making PostgreSQL ideal for high-traffic applications such as banking systems, e-commerce platforms, and large-scale web services.
Key Features of PostgreSQL
Advanced SQL Support
PostgreSQL provides rich SQL functionality, including complex and nested queries, subqueries and joins, views and updatable views, and aggregate and window functions. These features enable powerful data analysis directly within the database, reducing the need for excessive application-side processing.
Data Integrity and Reliability
Data correctness is fundamental for any database system. PostgreSQL ensures this through foreign key constraints to maintain referential integrity, check constraints to validate data, ACID-compliant transactions to guarantee consistency, and automatic crash recovery to prevent data loss.
Installation and Environment Setup
PostgreSQL can be installed by system administrators or individual users. In many operating systems, it may already be included as part of the distribution. If not, users can install it themselves without requiring superuser (root) access. Important environment variables include:
● PGHOST – Database server hostname
● PGPORT – Server port number (default: 5432)
● PGUSER – PostgreSQL username
Correct configuration of these variables ensures smooth connectivity between client applications and the database server.
PostgreSQL Installation on Windows (Step-by-Step)
Step 1: Download PostgreSQL
1. Open your browser and go to the official PostgreSQL website.
2. Click on Download.
3. Select Windows as the operating system.
4. Download the Windows installer (EXE) for the latest stable version.
Step 2: Run the Installer
1. Double-click the downloaded .exe
2. Click Yes if Windows asks for permission.
3. The PostgreSQL Setup Wizard will open → click Next.
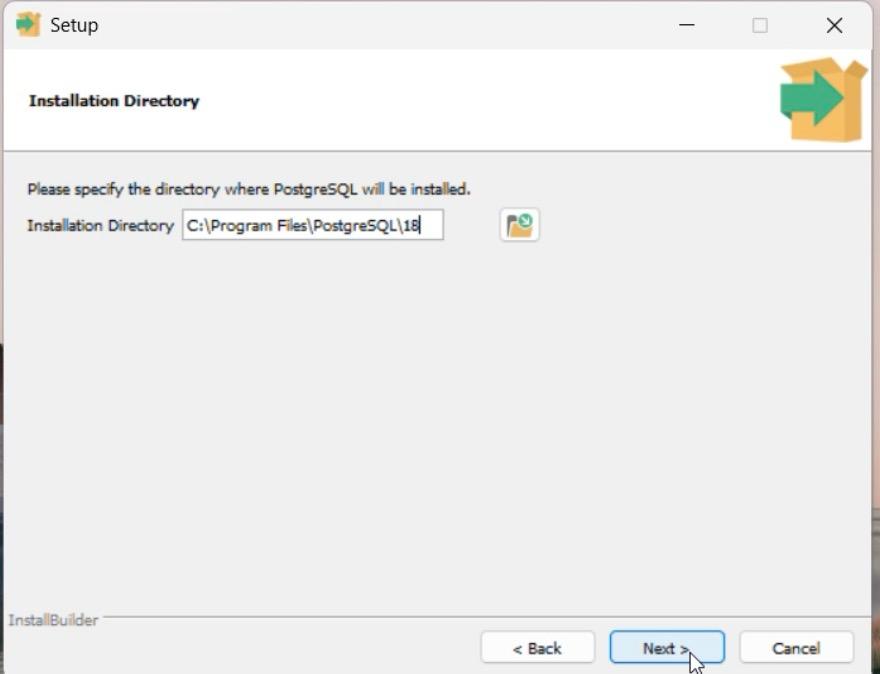
Step 3: Choose Installation Directory
Select the folder where PostgreSQL should be installed.
Default is recommended: C:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\
-
Click Next.
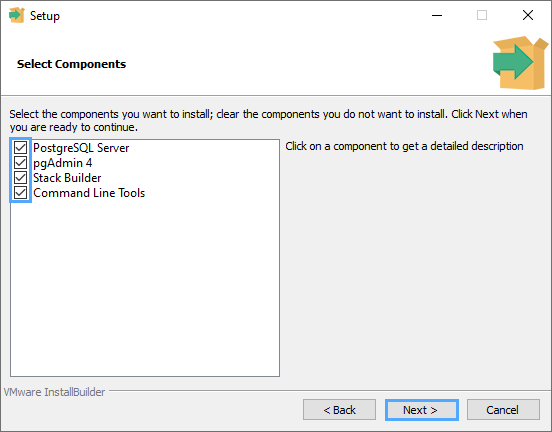
Step 4: Select Components
● Make sure the following are checked:
● PostgreSQL Server
● pgAdmin 4
● Command Line Tools
● Stack Builder
● Click Next.
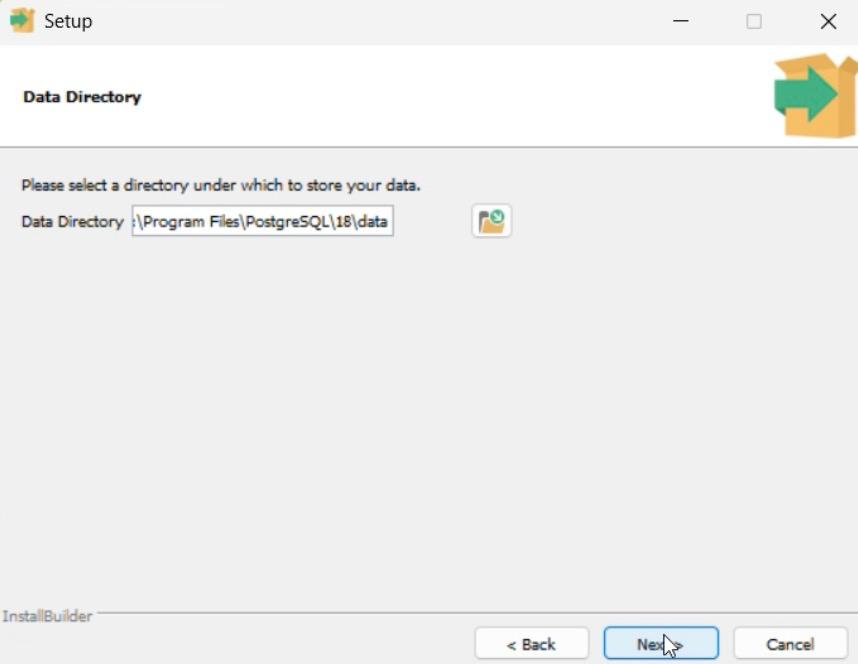
Step 5: Choose Data Directory
1. Select the location where database data will be stored.
Default is recommended.
2. Click Next.
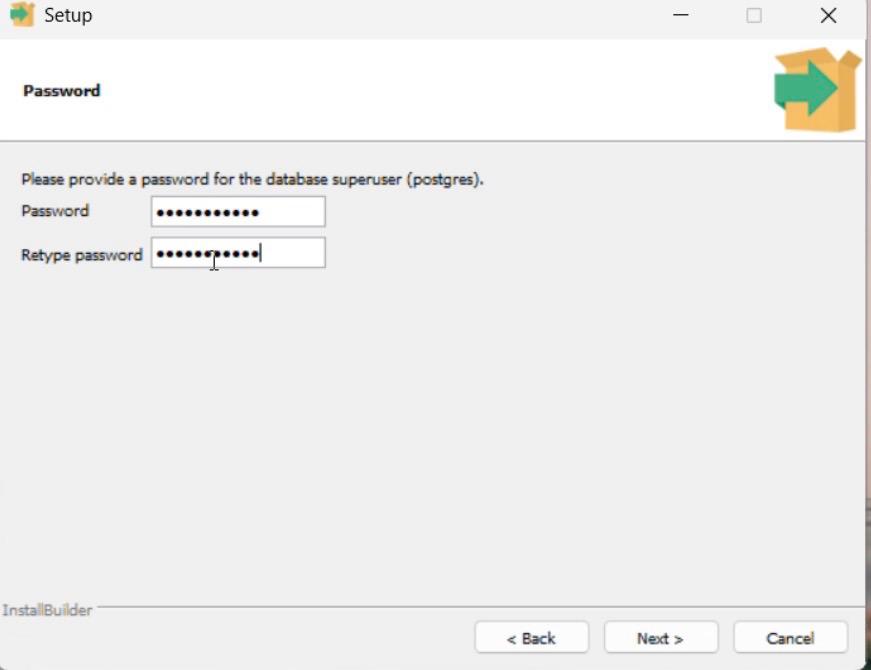
Step 6: Set Password
1. Enter a password for the PostgreSQL superuser (postgres).
2. Re-enter the password to confirm.
3. Remember this password — it is required to access PostgreSQL.
4. Click Next.
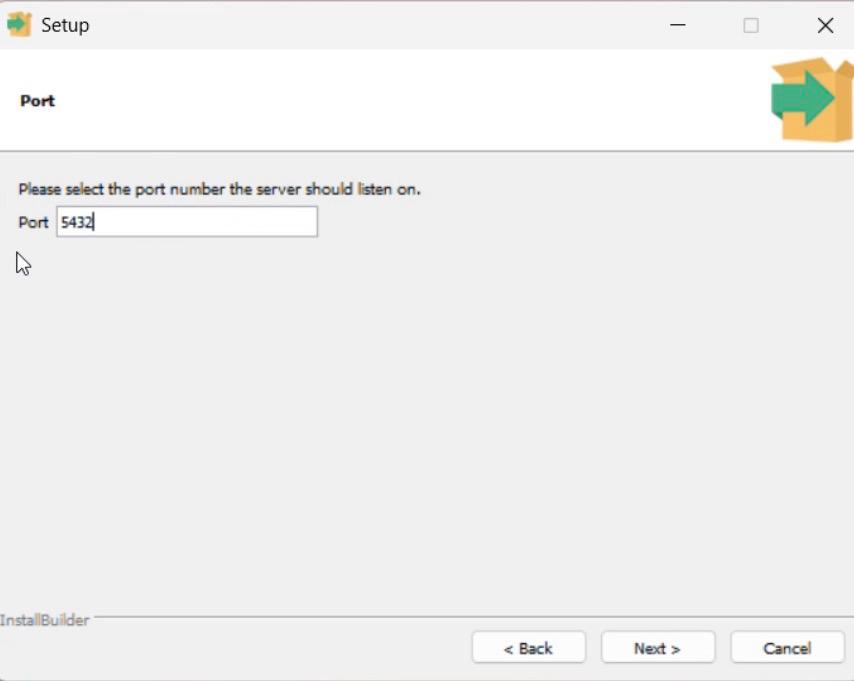
Step 7: Set Port Number
1. Default port is 5432.
2. Do not change unless required.
3. Click Next.
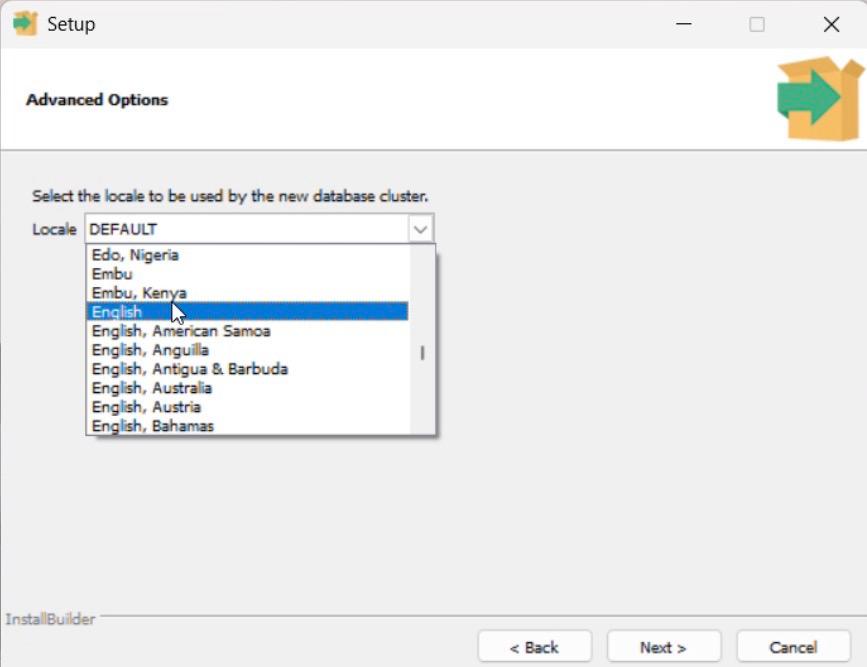
Step 8: Select Locale
1. Keep the default locale.
2. Click Next.
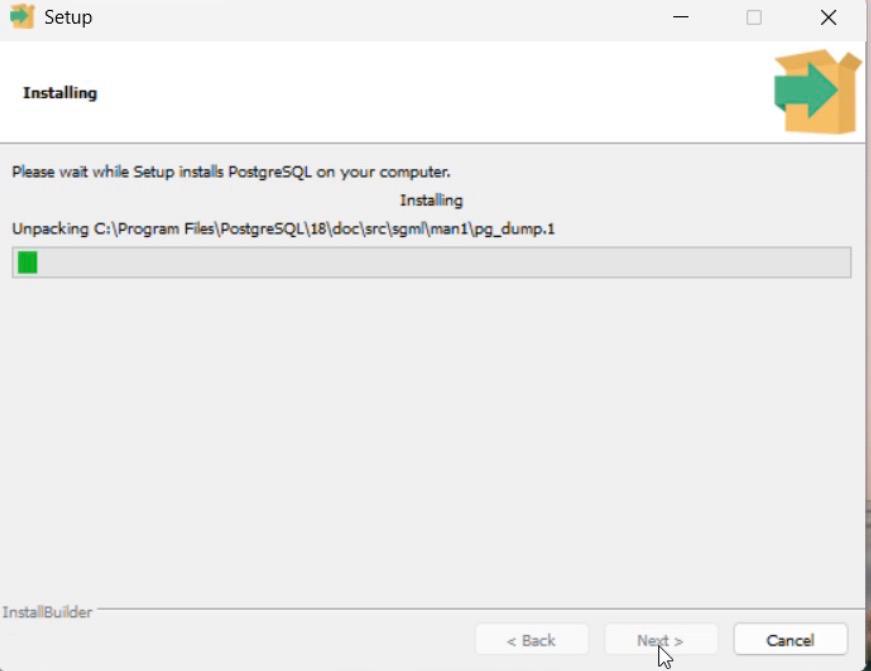
Step 9: Start Installation
1. Review the summary.
2. Click Next to begin installation.
3. Wait until the installation completes.
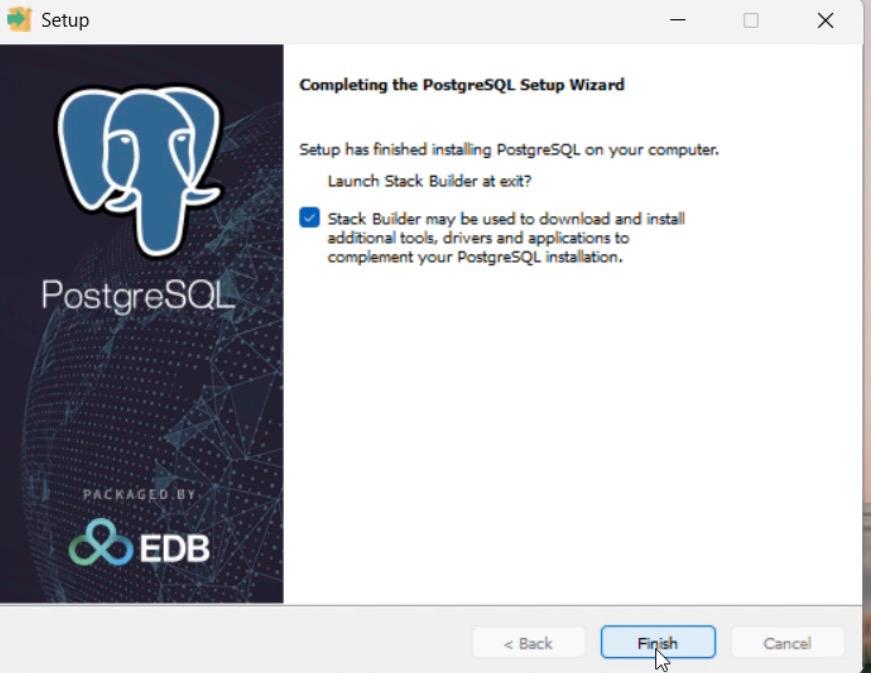
Step 10: Finish Setup
1. Click Finish.
2. Stack Builder may open (optional for add-ons).
Verify Installation
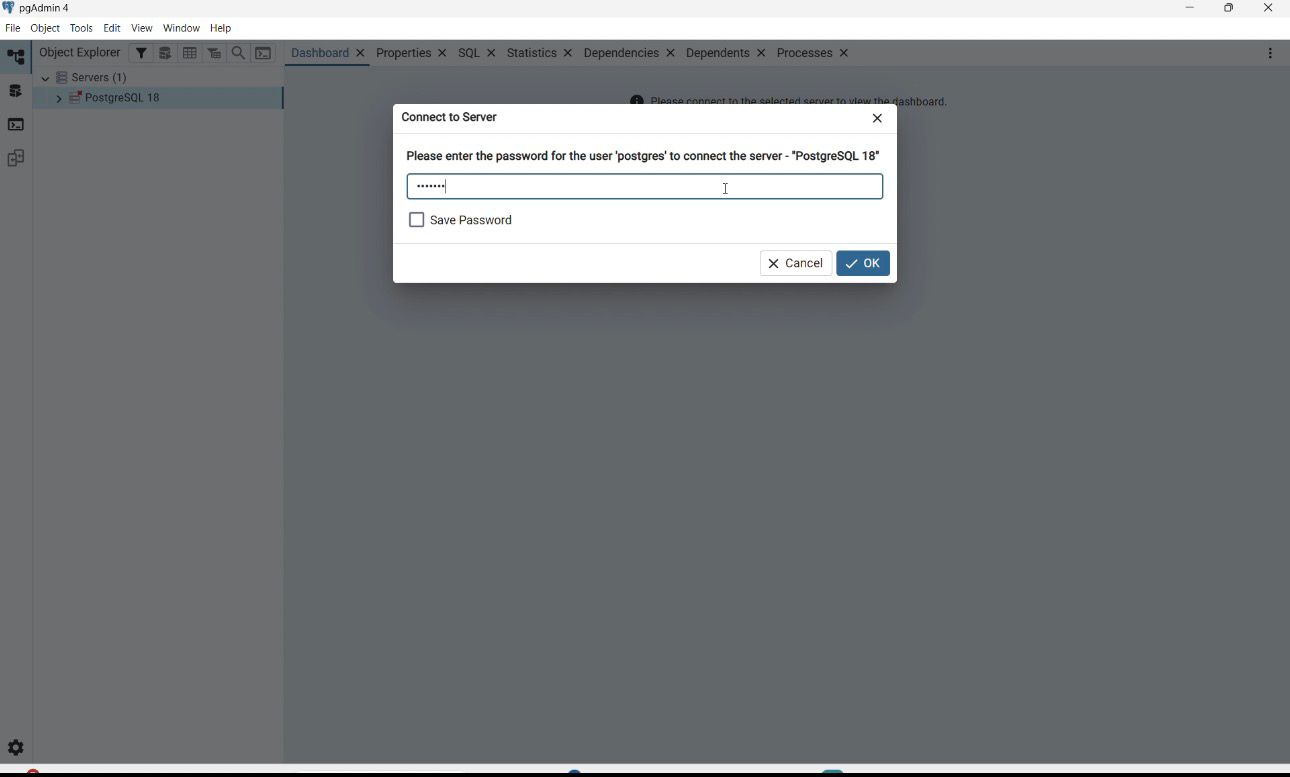
1. Open pgAdmin 4 from Start Menu.
2. Enter the password you set.
3. If pgAdmin opens successfully → PostgreSQL is installed correctly ✅
Verifying PostgreSQL Installation on Windows Using SQL Shell (psql)
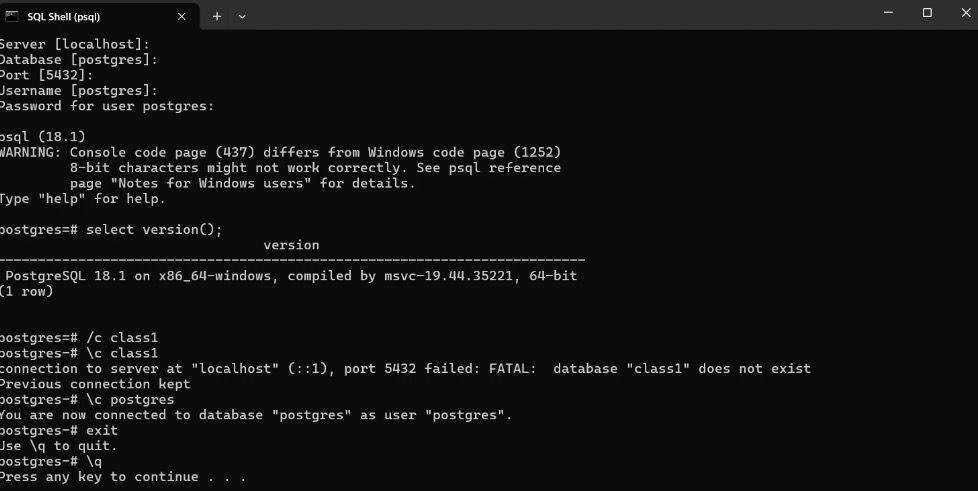
After installing PostgreSQL on Windows, SQL Shell (psql) is used to connect to the database server and validate that the installation is successful. The session below demonstrates the commonly used commands and their purpose during initial verification.
Connecting to PostgreSQL
● When SQL Shell (psql) starts, it prompts for connection details:
● Server: localhost
● Database: postgres
● Port: 5432
● Username: postgres
● Password: (password set during installation)
● Providing these details establishes a connection to the PostgreSQL server.
Command Used to Check PostgreSQL Version
SELECT version();
● This SQL command displays detailed information about the installed PostgreSQL version, operating system, and system architecture. The output confirms that PostgreSQL is installed correctly and running on a 64-bit Windows environment.
Command Used to Connect to Another Database
\c class1
● This meta-command attempts to connect to a database named class1. Since the database does not exist, PostgreSQL returns an error message indicating the database is not found, while keeping the current connection active.
Command Used to Reconnect to the Default Database
\c postgres
● This command reconnects the session to the default postgres database using the postgres user.
Command Used to Exit SQL Shell
\q
● This command exits the SQL Shell (psql) safely and closes the database session.
Bug Reporting and Community Support
Bug reports play a vital role in improving PostgreSQL. A good report includes exact steps to reproduce the problem, SQL scripts or test cases, complete error messages, and platform and version details. Before reporting, users should consult documentation, FAQs, and mailing lists to check if the issue is already known. PostgreSQL is supported by a strong global community through official documentation, wikis, FAQs, mailing lists, and discussion forums.
Conclusion
PostgreSQL is a mature, reliable, and highly extensible database management system that combines academic innovation with real-world performance. Its advanced SQL features, strong transactional integrity, robust architecture, and open-source flexibility make it suitable for both beginners learning database concepts and professionals building mission-critical systems. With powerful tools and an active global community, PostgreSQL continues to be a leading choice for modern data-driven applications.
Author : Geethika Bandaru
LinkedIn : http://linkedin.com/in/bandaru-geethika
Thank you for giving your valuable time to read the above information. Please click here to subscribe for further updates.
KTExperts is always active on social media platforms.
Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/ktexperts
LinkedIn : https://www.linkedin.com/company/ktexperts/
Twitter : https://twitter.com/ktexpertsadmin
YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/c/ktexperts
Instagram : https://www.instagram.com/knowledgesharingplatform
Note: Please test scripts in Non Prod before trying in Production.