PostgreSQL Commands and Data Types – A Complete Overview
Introduction
PostgreSQL is a powerful, open-source relational database management system widely used in modern applications. It is known for its reliability, performance, and rich support for advanced data types. Understanding SQL commands and PostgreSQL data types is essential for anyone working with databases, backend development, or data engineering.
This article provides a clear and structured explanation of SQL command categories and PostgreSQL data types, supported by practical examples.
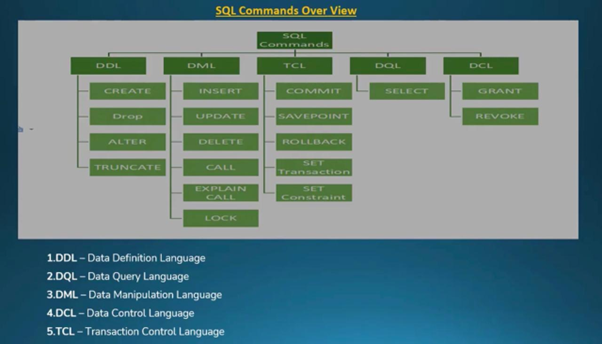
SQL Commands Overview
SQL commands are grouped based on their purpose in database operations.
1. Data Definition Language (DDL)
DDL commands are used to define, modify, and remove database structures.
Key DDL Commands
● CREATE – Creates database objects such as tables, views, indexes
● ALTER – Modifies the structure of an existing object
● DROP – Permanently deletes a database object
● TRUNCATE – Removes all records from a table without logging individual row deletions
Example
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
CREATE TABLE student ( student_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, name TEXT, age INTEGER ); DDL commands affect the structure of the database rather than the data itself. |
2. Data Manipulation Language (DML)
DML commands are used to manipulate data stored in database tables.
Key DML Commands
● INSERT – Adds new records
● UPDATE – Modifies existing records
● DELETE – Removes records
● CALL – Executes stored procedures
● LOCK – Controls concurrent access
Example
|
1 2 |
INSERT INTO student (name, age) VALUES ('Geethika', 21); |
3. Data Query Language (DQL)
DQL focuses on retrieving data from the database.
|
1 2 |
SELECT name, age FROM student; DQL allows filtering, sorting, grouping, and joining data. |
4. Data Control Language (DCL)
DCL commands control access and permissions.
● GRANT – Assigns privileges
● REVOKE – Removes privileges
|
1 |
GRANT SELECT ON student TO user1; |
5. Transaction Control Language (TCL)
TCL commands manage transactions to maintain consistency.
● COMMIT
● ROLLBACK
● SAVEPOINT
● SET TRANSACTION
These commands ensure ACID properties (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability).
PostgreSQL Numeric Data Types: PostgreSQL provides several numeric data types for storing integers and decimal values.
Numeric Data Types: Numeric data types store whole numbers and decimal values.
Type |
Storage |
Description |
smallint |
2 bytes |
Small integers |
integer |
4 bytes |
Typical integers |
bigint |
8 bytes |
Large integers |
decimal / numeric |
Variable |
Exact precision |
real |
4 bytes |
Floating-point (6 digits) |
double precision |
8 bytes |
Floating-point (15 digits) |
serial |
4 bytes |
Auto-increment |
bigserial |
8 bytes |
Large auto-increment |
Character Data Types: Character data types store text.
Type |
Description |
char(n) |
Fixed-length string |
character(n) |
Same as char |
varchar(n) |
Variable-length string |
character varying(n) |
Same as varchar |
text |
Unlimited length |
PostgreSQL internally treats varchar and text similarly, making text a popular choice.
Date and Time Data Types: PostgreSQL provides advanced support for date and time operations.
Type |
Description |
timestamp |
Date and time without time zone |
timestamptz |
Date and time with time zone |
date |
Date only |
time |
Time only |
interval |
Time interval |
Boolean and Enumerated Types
Boolean Type
Stores logical values:
TRUE or FALSE
Enumerated (ENUM) Type
● Defines a fixed set of allowed values.
● CREATE TYPE week AS ENUM (‘Mon’,’Tue’,’Wed’,’Thu’,’Fri’,’Sat’,’Sun’);
● ENUM improves data consistency and readability.
Geometric Data Types
Used for spatial and geometric data.
Type |
Description |
point |
Point on a plane |
line |
Infinite line |
lseg |
Line segment |
box |
Rectangular box |
path |
Open or closed path |
polygon |
Polygon |
circle |
Circle |
These are useful in GIS and spatial applications.
Network Address Types
Used to store network-related information.
Type |
Description |
cidr |
IPv4 / IPv6 networks |
inet |
IPv4 / IPv6 hosts |
macaddr |
MAC addresses |
They provide built-in validation and network operators.
Bit String Types
Used to store binary values.
● bit(n) – Fixed-length
● bit varying(n) – Variable-length
Often used for bit masks and flags.
Text Search Types
PostgreSQL supports full-text search
Type |
Description |
tsvector |
Stores searchable document |
tsquery |
Stores search query |
Used in search engines and document indexing systems.
UUID Type: UUIDs ensure global uniqueness.
Example:
550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000
Ideal for distributed systems and microservices.
XML Data Type
● Used to store XML documents.
● XMLPARSE(DOCUMENT ‘<tutorial><title>PostgreSQL</title></tutorial>’)
● Allows structured XML storage and querying.
JSON Data Type
● Stores JSON data with validation and operators.
|
1 2 3 |
row_to_json(row(1,'foo')); array_to_json(ARRAY[1,5,99,100]); Widely used in modern applications. |
Array Data Type
Allows columns to store multiple values.
Example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
CREATE TABLE monthly_savings ( name TEXT, saving_per_quarter INTEGER[], scheme TEXT[][] ); Useful for multi-valued attributes. |
Composite Types
Composite types represent structured records.
Example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
CREATE TYPE inventory_item AS ( name TEXT, supplier_id INTEGER, price NUMERIC ); They simplify complex data modeling. |
Range Types
Range types store intervals of values.
Built-in Range Types
● int4range
● int8range
● numrange
● tsrange
● tstzrange
● daterange
Example
|
1 2 |
SELECT daterange('2025-01-01','2025-01-31'); Range types are useful for bookings, schedules, and validity periods. |
Conclusion
PostgreSQL is a feature-rich database system that goes beyond traditional relational databases. Its extensive SQL command support and powerful data types enable developers to model real-world data efficiently and accurately. Mastering these concepts equips learners and professionals with the skills needed to build scalable, reliable, and high-performance applications.
Author : Geethika Bandaru
LinkedIn : http://linkedin.com/in/bandaru-geethika
Thank you for giving your valuable time to read the above information. Please click here to subscribe for further updates.
KTExperts is always active on social media platforms.
Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/ktexperts
LinkedIn : https://www.linkedin.com/company/ktexperts/
Twitter : https://twitter.com/ktexpertsadmin
YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/c/ktexperts
Instagram : https://www.instagram.com/knowledgesharingplatform
Note: Please test scripts in Non Prod before trying in Production.