Matadata (INFORMATION_SCHEMA)

WHAT IS METADATA ?
As per definition it is DATA ABOUT DATA. In MySQL METADATA stored in INFORMATION_SCHEMA.
INFORMATION_SCHEMA provides access to database metadata, information about the MySQL server such as the name of a database or table, the data type of a column, or access privileges. INFORMATION_SCHEMA is a database within each MySQL instance, the place that stores information about all the other databases that the MySQL server maintains. The INFORMATION_SCHEMA database contains several read-only tables. They are actually views, not base tables, so there are no files associated with them, and you cannot set triggers on them. Also, there is no database directory with that name. Although you can select INFORMATION_SCHEMA as the default database with a USE statement, you can only read the contents of tables, not perform INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE operations on them.
You can access Information_Schema in 3 ways.
- Using Information_schema tables.
- Using SHOW command.
- Using mysqlshow client program.
1.INFORMATION_SCHEMA :
- Data about schema’s and their objects(tables etc.)
First check the databases list
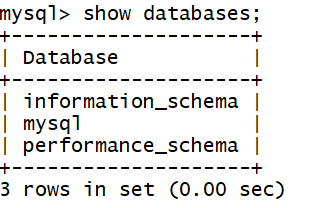
Connect to INFORMATION_SCHEMA database;
|
1 2 3 4 |
mysql> use information_schema; Reading table information for completion of table and column names You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A Database changed |
List out all the tables.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 |
mysql> SHOW TABLES; +---------------------------------------+ | Tables_in_information_schema | +---------------------------------------+ | CHARACTER_SETS | | COLLATIONS | | COLLATION_CHARACTER_SET_APPLICABILITY | | COLUMNS | | COLUMN_PRIVILEGES | | ENGINES | | EVENTS | | FILES | | GLOBAL_STATUS | | GLOBAL_VARIABLES | | KEY_COLUMN_USAGE | | OPTIMIZER_TRACE | | PARAMETERS | | PARTITIONS | | PLUGINS | | PROCESSLIST | | PROFILING | | REFERENTIAL_CONSTRAINTS | | ROUTINES | | SCHEMATA | | SCHEMA_PRIVILEGES | | SESSION_STATUS | | SESSION_VARIABLES | | STATISTICS | | TABLES | | TABLESPACES | | TABLE_CONSTRAINTS | | TABLE_PRIVILEGES | | TRIGGERS | | USER_PRIVILEGES | | VIEWS | | INNODB_LOCKS | | INNODB_TRX | | INNODB_SYS_DATAFILES | | INNODB_LOCK_WAITS | | INNODB_SYS_TABLESTATS | | INNODB_CMP | | INNODB_METRICS | | INNODB_CMP_RESET | | INNODB_CMP_PER_INDEX | | INNODB_CMPMEM_RESET | | INNODB_FT_DELETED | | INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE_LRU | | INNODB_SYS_FOREIGN | | INNODB_SYS_COLUMNS | | INNODB_SYS_INDEXES | | INNODB_FT_DEFAULT_STOPWORD | | INNODB_SYS_FIELDS | | INNODB_CMP_PER_INDEX_RESET | | INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE | | INNODB_CMPMEM | | INNODB_FT_INDEX_TABLE | | INNODB_FT_BEING_DELETED | | INNODB_SYS_TABLESPACES | | INNODB_FT_INDEX_CACHE | | INNODB_SYS_FOREIGN_COLS | | INNODB_SYS_TABLES | | INNODB_BUFFER_POOL_STATS | | INNODB_FT_CONFIG | +---------------------------------------+ 59 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
In above tables list the table name it self tables .
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
mysql> DESC TABLES; +-----------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-----------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | TABLE_CATALOG | varchar(512) | NO | | | | | TABLE_SCHEMA | varchar(64) | NO | | | | | TABLE_NAME | varchar(64) | NO | | | | | TABLE_TYPE | varchar(64) | NO | | | | | ENGINE | varchar(64) | YES | | NULL | | | VERSION | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | | | ROW_FORMAT | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | | | TABLE_ROWS | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | | | AVG_ROW_LENGTH | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | | | DATA_LENGTH | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | | | MAX_DATA_LENGTH | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | | | INDEX_LENGTH | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | | | DATA_FREE | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | | | AUTO_INCREMENT | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | | | CREATE_TIME | datetime | YES | | NULL | | | UPDATE_TIME | datetime | YES | | NULL | | | CHECK_TIME | datetime | YES | | NULL | | | TABLE_COLLATION | varchar(32) | YES | | NULL | | | CHECKSUM | bigint(21) unsigned | YES | | NULL | | | CREATE_OPTIONS | varchar(255) | YES | | NULL | | | TABLE_COMMENT | varchar(2048) | NO | | | | +-----------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 21 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
Try to get few column details
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
mysql> SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA,TABLE_NAME,TABLE_TYPE,ENGINE FROM TABLES LIMIT 10; +--------------------+---------------------------------------+-------------+--------+ | TABLE_SCHEMA | TABLE_NAME | TABLE_TYPE | ENGINE | +--------------------+---------------------------------------+-------------+--------+ | information_schema | CHARACTER_SETS | SYSTEM VIEW | MEMORY | | information_schema | COLLATIONS | SYSTEM VIEW | MEMORY | | information_schema | COLLATION_CHARACTER_SET_APPLICABILITY | SYSTEM VIEW | MEMORY | | information_schema | COLUMNS | SYSTEM VIEW | MyISAM | | information_schema | COLUMN_PRIVILEGES | SYSTEM VIEW | MEMORY | | information_schema | ENGINES | SYSTEM VIEW | MEMORY | | information_schema | EVENTS | SYSTEM VIEW | MyISAM | | information_schema | FILES | SYSTEM VIEW | MEMORY | | information_schema | GLOBAL_STATUS | SYSTEM VIEW | MEMORY | | information_schema | GLOBAL_VARIABLES | SYSTEM VIEW | MEMORY | +--------------------+---------------------------------------+-------------+--------+ 10 rows in set (0.01 sec) |
We can another database metadata using TABLES table.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
mysql> SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA,TABLE_NAME,TABLE_TYPE,ENGINE FROM TABLES WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA='world'; +--------------+-----------------+------------+--------+ | TABLE_SCHEMA | TABLE_NAME | TABLE_TYPE | ENGINE | +--------------+-----------------+------------+--------+ | world | city | BASE TABLE | InnoDB | | world | country | BASE TABLE | InnoDB | | world | countrylanguage | BASE TABLE | InnoDB | +--------------+-----------------+------------+--------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
Create test table in world databases with different engines.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
mysql> create table world.test(ID INT) ENGINE =MyISAM; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA,TABLE_NAME,TABLE_TYPE,ENGINE FROM TABLES WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA='world'; +--------------+-----------------+------------+--------+ | TABLE_SCHEMA | TABLE_NAME | TABLE_TYPE | ENGINE | +--------------+-----------------+------------+--------+ | world | city | BASE TABLE | InnoDB | | world | country | BASE TABLE | InnoDB | | world | countrylanguage | BASE TABLE | InnoDB | | world | test | BASE TABLE | MyISAM | +--------------+-----------------+------------+--------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
In above lines i have created object called test by sitting database information_schema but in syntax i have specified world.test means object will be created under world database .
Another way to check engine for a object using show create command.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
mysql> show create table world.test\G *************************** 1. row *************************** Table: test Create Table: CREATE TABLE `test` ( `ID` int(11) DEFAULT NULL ) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
To check the size of the tables we have two important variables DATA_LENGTH & INDEX_LENGTH
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
mysql> SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA,TABLE_NAME,TABLE_TYPE,ENGINE,DATA_LENGTH,INDEX_LENGTH FROM TABLES WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA='world'; +--------------+-----------------+------------+--------+-------------+--------------+ | TABLE_SCHEMA | TABLE_NAME | TABLE_TYPE | ENGINE | DATA_LENGTH | INDEX_LENGTH | +--------------+-----------------+------------+--------+-------------+--------------+ | world | city | BASE TABLE | InnoDB | 409600 | 131072 | | world | country | BASE TABLE | InnoDB | 98304 | 0 | | world | countrylanguage | BASE TABLE | InnoDB | 98304 | 65536 | | world | test | BASE TABLE | MyISAM | 0 | 1024 | +--------------+-----------------+------------+--------+-------------+--------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
To check exact size(bytes) of table we need to sum both DATA_LENGTH & INDEX_LENGTH
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
mysql> SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA,TABLE_NAME,TABLE_TYPE,ENGINE,DATA_LENGTH+INDEX_LENGTH as "TABLE SIZE"FROM TABLES WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA='world'; +--------------+-----------------+------------+--------+------------+ | TABLE_SCHEMA | TABLE_NAME | TABLE_TYPE | ENGINE | TABLE SIZE | +--------------+-----------------+------------+--------+------------+ | world | city | BASE TABLE | InnoDB | 540672 | | world | country | BASE TABLE | InnoDB | 98304 | | world | countrylanguage | BASE TABLE | InnoDB | 163840 | | world | test | BASE TABLE | MyISAM | 1024 | +--------------+-----------------+------------+--------+------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA,TABLE_NAME,TABLE_TYPE,ENGINE,(DATA_LENGTH+INDEX_LENGTH)/(1024*1024) as "TABLE SIZE in MB" FROM TABLES WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA='world'; +--------------+-----------------+------------+--------+------------------+ | TABLE_SCHEMA | TABLE_NAME | TABLE_TYPE | ENGINE | TABLE SIZE in MB | +--------------+-----------------+------------+--------+------------------+ | world | city | BASE TABLE | InnoDB | 0.5156 | | world | country | BASE TABLE | InnoDB | 0.0938 | | world | countrylanguage | BASE TABLE | InnoDB | 0.1563 | | world | test | BASE TABLE | MyISAM | 0.0010 | +--------------+-----------------+------------+--------+------------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
To check database size’s we use group by clause.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
mysql> SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA,TABLE_NAME,TABLE_TYPE,ENGINE,(DATA_LENGTH+INDEX_LENGTH)/(1024*1024) as "TABLE SIZE in MB" FROM TABLES GROUP BY TABLE_SCHEMA; +--------------------+----------------+-------------+--------------------+------------------+ | TABLE_SCHEMA | TABLE_NAME | TABLE_TYPE | ENGINE | TABLE SIZE in MB | +--------------------+----------------+-------------+--------------------+------------------+ | information_schema | CHARACTER_SETS | SYSTEM VIEW | MEMORY | 0.0000 | | mysql | columns_priv | BASE TABLE | MyISAM | 0.0039 | | performance_schema | accounts | BASE TABLE | PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA | 0.0000 | | world | city | BASE TABLE | InnoDB | 0.5156 | +--------------------+----------------+-------------+--------------------+------------------+ 4 rows in set (0.02 sec) |
Let’s say i want to convert all tables into InnoDB.
Example :
Tables are MyISAM.(100 tables)
We need to convert all tables to InnoDB which are in world database
To check which object is under which engine the preferred way is follows
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
mysql> select table_name,engine from TABLES where table_schema='world' and engine='MyISAM'; +------------+--------+ | table_name | engine | +------------+--------+ | test | MyISAM | +------------+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
Here i found only one object under MyISAM engine .
we need query to change into InnoDB then follow below command.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
mysql> select CONCAT ("ALTER TABLE ",table_name, "ENGINE =InnoDB;") from TABLES where table_schema='world' and engine='MyISAM'; +-------------------------------------------------------+ | CONCAT ("ALTER TABLE ",table_name, "ENGINE =InnoDB;") | +-------------------------------------------------------+ | ALTER TABLE testENGINE =InnoDB; | +-------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
In above command we used concat to get a query to change ENGINES . It will be useful when we have lots of tables to change.
Before changing will create few more tables test2 & test 3 .
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
mysql> create table world.test2(ID int) ENGINE=MyISAM; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> create table world.test3(ID int) ENGINE=MyISAM; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select CONCAT ("ALTER TABLE ",table_name, " ENGINE =InnoDB;") from TABLES where table_schema='world' and engine='MyISAM'; +--------------------------------------------------------+ | CONCAT ("ALTER TABLE ",table_name, " ENGINE =InnoDB;") | +--------------------------------------------------------+ | ALTER TABLE test ENGINE =InnoDB; | | ALTER TABLE test2 ENGINE =InnoDB; | | ALTER TABLE test3 ENGINE =InnoDB; | +--------------------------------------------------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
Now we can execute commands one by one are we can write as script .
It takes time depends on size of your table.
Let’s say If a table is 20 or 30 GB where takes 20 mins of time. That’s the reason we do changing engine only in maintenance window.
If we execute any of the statements will see the output.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
mysql> ALTER TABLE world.test ENGINE =InnoDB; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> select CONCAT ("ALTER TABLE ",table_name, " ENGINE =InnoDB;") from TABLES where table_schema='world' and engine='MyISAM'; +--------------------------------------------------------+ | CONCAT ("ALTER TABLE ",table_name, " ENGINE =InnoDB;") | +--------------------------------------------------------+ | ALTER TABLE test2 ENGINE =InnoDB; | | ALTER TABLE test3 ENGINE =InnoDB; | +--------------------------------------------------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
Then we can write a query like to find all the tables which has column ID, below example we are using COLUMNS table in information_schema.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
mysql> select TABLE_SCHEMA,TABLE_NAME,COLUMN_NAME from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS WHERE COLUMN_NAME LIKE 'ID'; +--------------------+-------------------------+-------------+ | TABLE_SCHEMA | TABLE_NAME | COLUMN_NAME | +--------------------+-------------------------+-------------+ | information_schema | COLLATIONS | ID | | information_schema | PROCESSLIST | ID | | information_schema | INNODB_SYS_FOREIGN | ID | | information_schema | INNODB_SYS_FOREIGN_COLS | ID | | mysql | slave_relay_log_info | Id | | mysql | slave_worker_info | Id | | world | city | ID | | world | test | ID | | world | test2 | ID | | world | test3 | ID | +--------------------+-------------------------+-------------+ 10 rows in set (0.01 sec) |
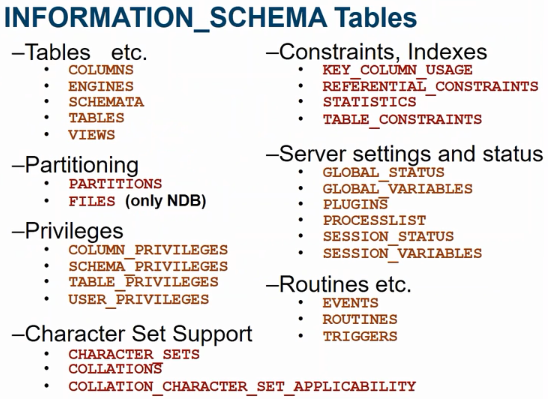
INFORMATION_SCHEMA database contains 59 tables but categorized into 7 groups.
We can check how database was created using show commands
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
mysql> show create database world\G *************************** 1. row *************************** Database: world Create Database: CREATE DATABASE `world` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET latin1 */ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
By default database uses latin character set .
To list out all character sets we use following commands.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 |
mysql> Show character set; +----------+-----------------------------+---------------------+--------+ | Charset | Description | Default collation | Maxlen | +----------+-----------------------------+---------------------+--------+ | big5 | Big5 Traditional Chinese | big5_chinese_ci | 2 | | dec8 | DEC West European | dec8_swedish_ci | 1 | | cp850 | DOS West European | cp850_general_ci | 1 | | hp8 | HP West European | hp8_english_ci | 1 | | koi8r | KOI8-R Relcom Russian | koi8r_general_ci | 1 | | latin1 | cp1252 West European | latin1_swedish_ci | 1 | | latin2 | ISO 8859-2 Central European | latin2_general_ci | 1 | | swe7 | 7bit Swedish | swe7_swedish_ci | 1 | | ascii | US ASCII | ascii_general_ci | 1 | | ujis | EUC-JP Japanese | ujis_japanese_ci | 3 | | sjis | Shift-JIS Japanese | sjis_japanese_ci | 2 | | hebrew | ISO 8859-8 Hebrew | hebrew_general_ci | 1 | | tis620 | TIS620 Thai | tis620_thai_ci | 1 | | euckr | EUC-KR Korean | euckr_korean_ci | 2 | | koi8u | KOI8-U Ukrainian | koi8u_general_ci | 1 | | gb2312 | GB2312 Simplified Chinese | gb2312_chinese_ci | 2 | | greek | ISO 8859-7 Greek | greek_general_ci | 1 | | cp1250 | Windows Central European | cp1250_general_ci | 1 | | gbk | GBK Simplified Chinese | gbk_chinese_ci | 2 | | latin5 | ISO 8859-9 Turkish | latin5_turkish_ci | 1 | | armscii8 | ARMSCII-8 Armenian | armscii8_general_ci | 1 | | utf8 | UTF-8 Unicode | utf8_general_ci | 3 | | ucs2 | UCS-2 Unicode | ucs2_general_ci | 2 | | cp866 | DOS Russian | cp866_general_ci | 1 | | keybcs2 | DOS Kamenicky Czech-Slovak | keybcs2_general_ci | 1 | | macce | Mac Central European | macce_general_ci | 1 | | macroman | Mac West European | macroman_general_ci | 1 | | cp852 | DOS Central European | cp852_general_ci | 1 | | latin7 | ISO 8859-13 Baltic | latin7_general_ci | 1 | | utf8mb4 | UTF-8 Unicode | utf8mb4_general_ci | 4 | | cp1251 | Windows Cyrillic | cp1251_general_ci | 1 | | utf16 | UTF-16 Unicode | utf16_general_ci | 4 | | utf16le | UTF-16LE Unicode | utf16le_general_ci | 4 | | cp1256 | Windows Arabic | cp1256_general_ci | 1 | | cp1257 | Windows Baltic | cp1257_general_ci | 1 | | utf32 | UTF-32 Unicode | utf32_general_ci | 4 | | binary | Binary pseudo charset | binary | 1 | | geostd8 | GEOSTD8 Georgian | geostd8_general_ci | 1 | | cp932 | SJIS for Windows Japanese | cp932_japanese_ci | 2 | | eucjpms | UJIS for Windows Japanese | eucjpms_japanese_ci | 3 | +----------+-----------------------------+---------------------+--------+ 40 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
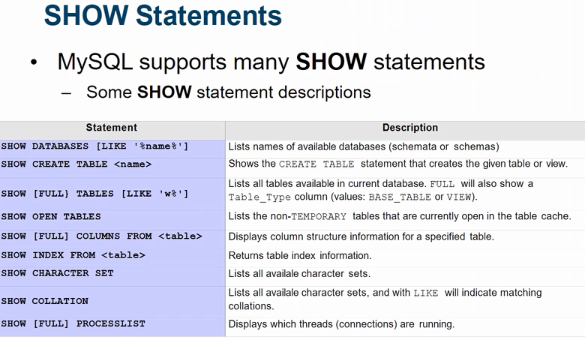
2.Using SHOW command.
There are various forms of MySQL SHOW commands, SHOW has many forms that provide information about databases, tables, columns, or status information about the server. This section describes those following:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 |
SHOW {BINARY | MASTER} LOGS SHOW BINLOG EVENTS [IN 'log_name'] [FROM pos] [LIMIT [offset,] row_count] SHOW CHARACTER SET [like_or_where] SHOW COLLATION [like_or_where] SHOW [FULL] COLUMNS FROM tbl_name [FROM db_name] [like_or_where] SHOW CREATE DATABASE db_name SHOW CREATE EVENT event_name SHOW CREATE FUNCTION func_name SHOW CREATE PROCEDURE proc_name SHOW CREATE TABLE tbl_name SHOW CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name SHOW CREATE VIEW view_name SHOW DATABASES [like_or_where] SHOW ENGINE engine_name {STATUS | MUTEX} SHOW [STORAGE] ENGINES SHOW ERRORS [LIMIT [offset,] row_count] SHOW EVENTS SHOW FUNCTION CODE func_name SHOW FUNCTION STATUS [like_or_where] SHOW GRANTS FOR user SHOW INDEX FROM tbl_name [FROM db_name] SHOW MASTER STATUS SHOW OPEN TABLES [FROM db_name] [like_or_where] SHOW PLUGINS SHOW PROCEDURE CODE proc_name SHOW PROCEDURE STATUS [like_or_where] SHOW PRIVILEGES SHOW [FULL] PROCESSLIST SHOW PROFILE [types] [FOR QUERY n] [OFFSET n] [LIMIT n] SHOW PROFILES SHOW RELAYLOG EVENTS [IN 'log_name'] [FROM pos] [LIMIT [offset,] row_count] SHOW SLAVE HOSTS SHOW SLAVE STATUS [FOR CHANNEL channel] SHOW [GLOBAL | SESSION] STATUS [like_or_where] SHOW TABLE STATUS [FROM db_name] [like_or_where] SHOW [FULL] TABLES [FROM db_name] [like_or_where] SHOW TRIGGERS [FROM db_name] [like_or_where] SHOW [GLOBAL | SESSION] VARIABLES [like_or_where] SHOW WARNINGS [LIMIT [offset,] row_count] |
Show statements :
Examples :
To list only tables
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
mysql> use world Reading table information for completion of table and column names You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A Database changed mysql> show full tables; +-----------------+------------+ | Tables_in_world | Table_type | +-----------------+------------+ | city | BASE TABLE | | country | BASE TABLE | | countrylanguage | BASE TABLE | | test | BASE TABLE | | test2 | BASE TABLE | | test3 | BASE TABLE | +-----------------+------------+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
Let’s create view on city table.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
mysql> Create view sampleview as select * from city; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) mysql> show tables; +-----------------+ | Tables_in_world | +-----------------+ | city | | country | | countrylanguage | | sampleview | | test | | test2 | | test3 | +-----------------+ 7 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> show full tables; +-----------------+------------+ | Tables_in_world | Table_type | +-----------------+------------+ | city | BASE TABLE | | country | BASE TABLE | | countrylanguage | BASE TABLE | | sampleview | VIEW | | test | BASE TABLE | | test2 | BASE TABLE | | test3 | BASE TABLE | +-----------------+------------+ 7 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
Here we have two commands show tables and show full tables .
Show tables will display all object names where as show full tables displays along with type of objects.
Example 2 :
To list out the databases starts with particular character .
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
mysql> show databases like 'w%'; +---------------+ | Database (w%) | +---------------+ | world | +---------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
To check tables with specific word.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
mysql> use information_schema; Reading table information for completion of table and column names You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A Database changed mysql> show tables like 'TABLE%'; +---------------------------------------+ | Tables_in_information_schema (TABLE%) | +---------------------------------------+ | TABLES | | TABLESPACES | | TABLE_CONSTRAINTS | | TABLE_PRIVILEGES | +---------------------------------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
3.Using mysqlshow client program.

The mysqlshow client can be used to quickly see which databases exist, their tables, or a table’s columns or indexes. Mysqlshow provides a command-line interface to several SQL SHOW statements. The same information can be obtained by using those statements directly. For example, you can issue them from the MySQL client program. This is command need to execute from linux prompt
Fetching information about databases using mysqlshow command.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
root@ip-172-31-14-134:~# mysqlshow -uroot -p Enter password: +--------------------+ | Databases | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | mysql | | performance_schema | | world | +--------------------+ |
Fetching information about tables list from world database.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
root@ip-172-31-14-134:~# mysqlshow -uroot -p world Enter password: Database: world +-----------------+ | Tables | +-----------------+ | city | | country | | countrylanguage | | sampleview | | test | | test2 | | test3 | +-----------------+ |
Fetching information about particular table using mysqlshow command.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
root@ip-172-31-14-134:~# mysqlshow -uroot -p world city Enter password: Database: world Table: city +-------------+----------+-------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+---------------------------------+---------+ | Field | Type | Collation | Null | Key | Default | Extra | Privileges | Comment | +-------------+----------+-------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+---------------------------------+---------+ | ID | int(11) | | NO | PRI | | auto_increment | select,insert,update,references | | | Name | char(35) | latin1_swedish_ci | NO | | | | select,insert,update,references | | | CountryCode | char(3) | latin1_swedish_ci | NO | MUL | | | select,insert,update,references | | | District | char(20) | latin1_swedish_ci | NO | | | | select,insert,update,references | | | Population | int(11) | | NO | | 0 | | select,insert,update,references | | +-------------+----------+-------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+---------------------------------+---------+ |
Fetching information about columns in a table using mysqlshow command.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
root@ip-172-31-14-134:~# mysqlshow -uroot -p world city ID Enter password: Database: world Table: city Wildcard: ID +-------+---------+-----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+---------------------------------+---------+ | Field | Type | Collation | Null | Key | Default | Extra | Privileges | Comment | +-------+---------+-----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+---------------------------------+---------+ | ID | int(11) | | NO | PRI | | auto_increment | select,insert,update,references | | +-------+---------+-----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+---------------------------------+---------+ |
Thank you for giving your valuable time to read the above information. Please click here to subscribe for further updates
KTEXPERTS is always active on below social media platforms.
Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/ktexperts/
LinkedIn : https://www.linkedin.com/company/ktexperts/
Twitter : https://twitter.com/ktexpertsadmin
YouTube : https://www.youtube.com/c/ktexperts
Instagram : https://www.instagram.com/knowledgesharingplatform




